Refugee
Daily Life
Your health is your physical, mental and social well-being. This section shows how to make your health a priority in daily life with important information on your coverage, how to maintain your health, and how to access essential services.
Health Coverage
Refugees resettling in Alberta immediately have access to health care services under the Interim-Federal Health Program (IFHP). The IFHP provides refugees with limited, temporary coverage of health-care benefits to protected persons, including Government Assisted Refugees (GARs), Privately Sponsored Refugees (PSRs), and refugee claimants. You will need to bring your IFH card with you every time you seek medical help. Determine your eligibility.
For information about what services are covered, see the Government of Canada.
In Alberta, refugees have supplementary coverage if they are eligible for the Alberta Adult Health Benefit, and the Alberta Child Health Benefit Program. These programs provide benefits like access to prescription and non-prescription drugs, diabetic supplies, ambulance services, and dental and optical care.
Refused services or expected to pay up-front costs? With recent changes to the IFHP, your service provider may not be familiar. Make sure you know your rights.
Health Care in Alberta
Health care in Canada is publicly funded. Most services are free of charge. Canadians see a doctor on a regular basis to maintain their health rather than seeing one when they are very sick or injured. Health can be affected by a variety of different factors, including but not limited to income and social status, education and literacy, employment and working conditions, social and physical environments, healthy child development, health services, gender, and culture.
We recommend you find a primary care physician. Like anyone moving into the province, you will need to apply for health coverage under the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. When you receive provincial coverage, you will receive a health card, and will need to show this at the hospital or medical clinic when you access services.
Keep in mind that most but not all services are covered under your health plan. Examples of services that require extra health coverage in Alberta include dental, prescription medications, physiotherapy, and prescription eye glasses. You will need to apply for extra coverage for these services or your employer may offer an insurance plan as part of your work.
It is recommended that you visit the Alberta Health Services Refugee Health Page: Alberta Health Services Refugee Health Page
Connect with a Doctor & Primary Care Networks
One of the first steps during your settlement journey is to find a family doctor. Your settlement agency or sponsor may help you find and connect with a family doctor. If you need medical assistance right away, you can go to a primary care network and present your health card. Here is where to find one:
- Find a Doctor – Alberta Health Services
- Finding a doctor and dentist –Government of Canada
- Primary Care Networks
Female Doctors
Do you require a female doctor? Just ask your health provider!
Call Health Link (811) for more information about the health care system and your health concerns.
Taking Care of Your Health – Preventing Illness and Living Well in Canada
This section will explore key information for maintaining your health in Canada, and preventing illness. You may not have had time to think about your health back home, but now is the time to give energy to taking care of yourself.
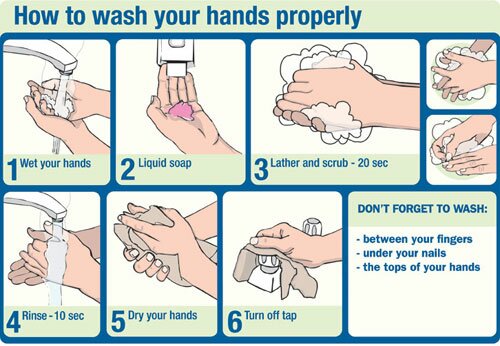
Hygiene – Prevent Disease!
Hand hygiene is the most important way to prevent the spread of germs, and stay healthy. It helps keep you healthy by reducing the number of germs on your hands and helps reduce the spread of germs to your family, friends, coworkers, residents or clients.
Wash your hands regularly. This means:
- Before, during and after preparing food
- Before eating food; before and after treating a cut or wound
- After going to the bathroom
- After blowing your nose; coughing or sneezing
- After touching an animal
- Animal feed, or animal waste
- After touching garbage
Exercise and Eat Well
The Canada Food Guide provides information on what foods to eat to stay healthy. The North American diet is high in sugar and fat which are things to stay away from. The Canada Food Guide provides more information in different languages on what foods to eat, and what foods to avoid. Eating well is another way to prevent disease.
Exercise is a great way to stay healthy and manage stress. Get outside, and explore the many parks and greenspaces in your community. Join a gym, or team. There are many ways to exercise. Hal and Joanne, Canadian health and lifestyle personalities, can show you how on their YouTube channel BodyBreak.
Take Care of Your Teeth
Oral health is important for your overall health. Learn more about dental health, and caring for children’s teeth. See the Healthy Smile, Happy Child Brochure. It may be challenging to get your child to brush their teeth, make it fun. Elmo can help! Going to a dentist is important for everyone. Reduced-fee dental treatment services by qualified dentists to families in financial need and without access to dental insurance are available in your community.
- Find a Dentist – Dental Health Alberta
- Finding a Dentist –Government of Canada
- Public Health – Dental Treatment Services (Reduced-fee)
- Canadian Dentists for Refugees
- The Alex Mobile Health Bus
Take Care of Your Mental Health and Emotional Wellness
Maintaining your mental health, like your physical health, is important! As a newcomer to Canada, you may experience stress in your new life. Stress is a normal part of transition and the resettlement process.
According to the Canadian Mental Health Association, mental health means finding a balance in all aspects of your life: social, physical, spiritual, economic and mental. When your mental health is not in balance, mental illness can occur, and can take various forms. It is important to remember that all mental illness can be treated, and in Canadian culture is nothing to be ashamed of. For more information about mental illness, see the Canadian Mental Health Association’s (CMHA) brochures.
The CMHA with the help of the Multicultural Health Brokers, have recently developed a mental health booklet in Arabic (pdf). It touches on the following subjects:
- Mental Health for Life
- Are you feeling Sad?
- Feeling Stressed
- PTSD
- Support a Loved One
- Getting Help
For information on how to access multi-lingual mental health services in Alberta:
- Inform Alberta
- Alberta Health Services
Settlement agencies can also connect people with mental health services.
For more information about mental health, see these Multi-Language Brochures
Crisis Centres
Talking anytime you need with a trained professional or volunteer can provides you with immediate support. 24 hour a day support is available across Alberta. You do not need to be in a serious crisis to call a helpline. You may call to obtain information or for referrals for local community services. Sometimes it’s just useful to chat about something on your mind that you want to talk over with someone outside of the situation. Of course, you should also always call the crisis phone line in your area when you are in emotional crisis. No problem is too small to call about. Call 911 if you need immediate medical assistance.
- What to expect when calling a helpline
- Find a Crisis Centre
Post-Traumatic Stress
Post-Traumatic Stress is one of the most common mental health challenges faced by refugees, and can occur at any time following a traumatic event. Many refugees have experiences of trauma, which, in some cases, may lead to Post Traumatic Stress. Symptoms include: nightmares, inability to sleep, irritability or quick to anger, feeling “on edge,” flashbacks to the event, panic or fear even though they are in a safe environment. Watch for signs of trauma and stress with your loved ones. Remember if you have symptoms, you are not alone!
It is important to know that services are available in your own language for any individual who has been affected by this illness, and other illnesses associated with mental health.
- Refugee Mental Health Matters Video
- Fact sheet: Understanding PTSD
Survivors of Torture Youth and Family Project
Under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, an individual is protected from cruel and unusual punishment. If you or a loved one are suffering from previous experiences of torture, services exist that can help you get the help you need. Specialty programming exists that builds community for refugee children and youth who have experienced torture or war-related violence: Survivors of Torture Youth and Family Project.
Creating Healthy Relationships
Abuse can happen to anyone, men or women, children, adults or older adults.
Unfortunately, the incidence of domestic violence increases following immigration to a new country, and is more common for women. Domestic violence is any assault occurring between intimate partners including past, present or potential partners. It includes many types of abuse: physical abuse (hitting, punching, kicking etc.), sexual abuse (include unwanted activity with spouse, partner, boyfriend or girlfriend, child), psychological / emotional abuse (threatening to hurt someone), financial abuse, or neglect.
Domestic violence is against the law in Canada.
Find out more, here: What do immigrants and refugees need to know about domestic abuse?
Are you in an abusive relationship? Get help. Nobody deserves to be treated this way.
If you are in immediate danger, call 911.
There are special organizations that support victims of abuse which provide shelter, counseling, legal advice and resources to flee violence across the province:
- Calgary
- Edmonton
- Red Deer
- Lethbridge
- Medicine Hat
- Brooks
Healthy Relationships with Your Children
Being a parent is rewarding, but it can be challenging. There are lots of resources to help keep your family healthy and happy:
- Information for Parents
- Healthy Parents Healthy Children
Parenting classes are available at your local settlement agency or library, or see here for more information:
- Birth & Babies
- Families Matter
Parenting and the Law
Parents must provide their children with the necessities of life and can be charged with a crime if they do not provide for their children under 16 years of age.
Sexual Health
Sexual health also plays a role in your physical health. Sexual health centres and clinics across Alberta provide sexual education, counselling services, and services such as pregnancy tests, cervical cancer screening, sexual transmitted disease tests, and birth control. These are all confidential services and can be provided by female doctors and staff.
For culturally appropriate information and programs, consult:
- Calgary Sexual Health Centre
- Compass Centre
- Alberta Health
- Alberta Health Services
- Action Canada for Sexual Health and Rights
Consent – No means NO
All sexual activity without consent is a crime regardless of age or marital status. Consent is to agree to engage in sexual activity. It is as simple as a cup of tea, see this video. Sexual assault is any type of forced or coerced sexual contact or behavior that happens without consent. If this happens to you, it is not your fault. There are resources to help with Sexual Assault and Abuse.
The general age of consent to sexual activity is 16 years. The age of consent is 18 years if the sexual activity occurs within a relationship of authority (e.g. teacher, coach, babysitter) or where it involves exploitative activity like prostitution. This brochure provides information about Canada’s laws on sexual assault: No Means No.
The legal age of marriage in Alberta is 18 years old. A parent’s consent is required to marry individuals under the age of 18 years old. This exception only applies to those who are 16 years old or older, unless that person is pregnant or the mother of a child. For more details please see the Marriage Act.
LGBTQ+
Being Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender or Queer (LGBTQ+) is accepted in Canada, and marrying someone of the same-sex is legal. According to section 15 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, LGBTQ+ people have a right to equality. Violence against the LGBTQ+ is a hate crime punishable under the Criminal Code. Please remember that homophobia is unacceptable in Canada. Learn about the Agarwal’s inspiring family story.
Please see our Community section for a full list of services.
Education is a core Canadian value and human right.
In Alberta, education is publicly funded and free of charge for all students from kindergarten until grade 12 (ages 5-18). Education is mandatory for students aged 6-16. Children typically attend classes at either a public, a separate (Catholic) or a francophone school board. Please note that some public and separate schools also provide education in French. Students who speak English as their second language can participate in an English as a Second Language Program (ESL) at school. Alberta society prides itself on its high-quality public education system.
Children can also attend a charter or a private school in Alberta. Charter schools are autonomous non-profit public schools designed to provide innovative or enhanced education programs that improve the acquisition of student skills, attitudes and knowledge in some measurable way. A private school is founded, conducted, and maintained by a private group rather than by the government, usually charging tuition and often following a particular philosophy. Be sure your private school is registered with Alberta Education.
Grade System
Elementary school runs from kindergarten until Grade 6. Junior High School (or middle school) is from Grade 7 until Grade 9. High school is from Grade 10 until Grade 12. The Grade Conversion Guide helps interpret foreign grades.
The Government of Alberta is an excellent source of information about the Alberta school system. The Newcomers Guide to Education – Elementary and the Alberta Teacher’s Association – Learning Together: Public Education in Alberta are also good resources, and are available in a range of languages.
School Calendar
The school year is from September until June with summer holidays during July and August. The day normally starts at 8:30am and ends at 3:00pm – this may vary from school to school. Each school board has a calendar on its website. Daily schedules can be found on the individual schools’ websites.
School Administration
Education is the responsibility of the provincial government, and the Minister of Education. School boards manage schools in the local area. Trustees are members of the school board, providing a link between the board and local communities. They are elected representatives.
Principals are the main leader in individual schools. They are responsible for making sure schools are welcoming and inclusive, principals are also in charge of student discipline. Teachers prepare student lessons, and run classrooms. They are in contact with parents about their children. Parents are invited to attend parent-teacher interviews with teachers a couple of times a year where they discuss how to ensure that students succeed. Meetings with teachers may be scheduled upon a parent’s request or if the teacher believes an extra meeting is necessary. Other school staff, like social workers, Settlement Workers in Schools (SWIS), and administration, also work in schools to help students and their families understand the school system.
For a greater understanding of the system, you are encouraged to visit:
Valuing All Students by Alberta Education
Education in Canada: An Overview by the Council of Ministers of Education, Canada (CMEC)
Settlement Workers in Schools (SWIS)
Your child’s school will likely have a SWIS worker available to help newcomer families and students. This person is a resource to you. They understand the challenges newcomers face starting school. Ask them about any questions you may have. It could be about anything you may need to know about. Ranging from how the school system works, banking, or mental health.
English as an Additional Language (EAL)
English as an Additional Language programs are available in many schools. These programs also help students learn the norms and customs of life in Canada.
Schools in Your Area
The following links will provide more information about each school board and will help you find a school in your area.
Calgary
Refugee Child Enhanced Integration Project: This project is designed to support refugee children and youth in the school system. It provides refugee children with the right support and services so they can be successful.
Elementary and Middle School Boards:
Public Schools:
- Calgary Board of Education (Calgary School District #19)(CBE)
Catholic Schools:
- Calgary Roman Catholic Separate School District No. 1, also called the Calgary Catholic School District.
Francophone Schools:
- Conseil Scolaire FrancoSud or The Southern Francophone Education Region No. 4, in English.
Charter Schools:
- Almadina Language Charter Academy:
- Calgary Arts Academy Society
- Calgary Girls’ School Society
- Connect Charter School
- Foundation for the Future Charter Academy
- Westmount Charter School
Edmonton
Elementary and Middle School Boards:
Public schools:
- Edmonton Public Schools (Edmonton School District #7)
Catholic Schools:
- Edmonton Catholic School District, also called Edmonton Catholic Separate School District #7
Francophone Schools:
- Conseil Scolaire Centre-Nord, or in English, Greater North Central Francophone Education Region No. 2)
Charter Schools:
- Aurora Academic Charter School
- Boyle Street Education Centre
- Mother Earth’s Children Charter School
- New Horizons School
- Suzuki Charter School
Red Deer
There are 28 schools: 13 elementary, 5 middle schools, 2 high schools, 8 alternative schools in Red Deer.
Public Schools:
- Red Deer Public School District, also called Red Deer Public School District No. 104
Catholic Schools:
- Red Deer Catholic Regional Schools (RDCRS), also called Red Deer Catholic Regional Division No. 39
Francophone Schools:
- Conseil Scolaire Centre-Nord, or in English, Greater North Central Francophone Education Region No. 2)
Lethbridge
Public Schools:
- Lethbridge School District No. 51
- Palliser Regional Schools
Catholic Schools:
- Holy Spirit Catholic Schools, also called Holy Spirit Roman Separate Regional Division No. 4
Medicine Hat
Public Schools:
- Medicine Hat School District No.#76
Catholic Schools:
- Medicine Hat Catholic Board of Education, also called Medicine Hat Catholic Separate Regional Division No. 20
Charter Schools:
- Centre for Academic and Personal Excellence – (CAPE) This public charter school runs from kindergarten to grade nine.
Brooks
Elementary and Middle School Boards:
Public Schools:
- Grasslands Public Schools (Grasslands Regional Division No 6)
Catholic Schools:
- Christ the Redeemer Catholic Schools, also called Christ the Redeemer Catholic Separate Regional Division No. 3
What is Bullying?
Bullying is a repeated and hostile or demeaning behaviour intended to cause harm, fear or distress, including psychological harm or harm to a person’s reputation. It often involves an imbalance of social or physical power.
Although it is prohibited behaviour in school, it is commonly found, and the impacts can be serious. To learn more, please visit:
Alberta Education – Bullying Prevention
Stop A Bully – Anti-Bullying Videos
Post-Secondary Education
After high school, young adults often attend post-secondary education which is not free; however, scholarships and bursaries do exist, and student loans are available. Students may also study outside of the province across Canada or abroad. For more information on post-secondary, and adult education, visit:
Alberta Advanced Education
Government of Canada – Adult and Post-secondary Education
Transferring International Education
If you have an international education, find out how to get assessed. View educational, transfer or assessment resources.
Start Planning your Post-secondary Pathway
Learn more about different occupations in Alberta and what type of education and training you will need. Get started with these career videos!
What is the Difference between College and University in Canada?
It is important to know the difference between College and University in Canada. It may mean something different to you. When selecting a post-secondary education, make sure it is the right fit for you and meets your career needs.
Universities
Universities offer academic and professional programs, and grant degrees at the bachelor, master or PhD levels. They are institutions of hiring learning at the highest level. Bachelor degrees are generally 3 to 4 years when taken full-time. Typically, during the summer months from May to September, there is no school. Master’s degrees may be 1 to 2 years long, and you must have a Bachelor degree to be accepted. Depending on the program, you may be offered some work doing research or teaching part-time at the school.
College
Offer applied arts and technology degrees. They offer practical and hands-on training. A program is shorter than at Universities at one year for a certificate and 2 or 3 years for a diploma.
For more information, see Settlement.org.
Tuition
When you take a post-secondary program, you have to pay tuition. See the tuition schedule for the specific program you want to take with an institution below. Financial aid is available from the provincial and federal government for students who demonstrate financial need. Bursaries and/or loans will be given to you. With loans, you will need to pay back once you graduate. To determine your financial need, the government compares your costs for education and living and what you can reasonably contribute.
Student Aid Alberta
Canada Student Loans Program
Students commonly work part-time at the same time as studying, to afford for their education.
The Immigrant Access Fund provides micro loans of up to $10,000 for internationally trained immigrants so they can obtain the Canadian licensing or training they need to work in their field. The loan can pay for exams, training, qualification assessments, professional association fees, books and course materials, living allowance and other expenses related to obtaining the Canadian licensing or training they need.
For a list of post-secondary education institutions in your area, see the list provided below.
Calgary
- Alberta College of Art and Design
- Bow Valley College
- University of Calgary
- Mount Royal University
- St. Mary’s University
- Ambrose University
- Alberta Bible College
- Southern Alberta Institute of Technology
- Cambrooks College
- Robertson College
- Reeves College
- Columbia College
- Makami College
Edmonton
- University of Alberta
- Northern Alberta Institute of Technology
- NorQuest College
- MaKami College
- Robertson College
- Reeves College
- Concordia University of Edmonton
- Taylor Seminary
- Alberta Caregiving Institute
Red Deer
- Red Deer College
Lethbridge
- Lethbridge College
- University of Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
- Medicine Hat College
Brooks
There are no colleges or universities in Brooks.
When you come to Canada, one of your top priorities will be improving your language skills. This section will provide you with information on how to access language services, and tools to build your language skills. For when you need extra support, interpretation and translation services are available which is also discussed below.
Improving Your Language Skills
Canada has two official languages: English and French. While some Albertans speak French, English is more common. Learning to speak, read and write in English will help you succeed in Canada. This is one of your core responsibilities during the sponsorship period or during the RAP program. You will likely need to develop your English skills before looking for a job.
You can increase your proficiency in the English language by accessing different types of language training such as classes and conversation circles. Classes are provided by service providers and academic institutions. They also provide information on settlement, employment, education, and offer literacy programs. One of the classes accessed by Government Assisted Refugees (GARs) is the Language Instruction for Newcomer Canadians (LINC) program. English as a Second Language (ESL) courses are also popular. Many ESL programs do have a fee to use the services, but some ESL programs may be able to provide funding for these classes. Make sure to check with your course provider to see if funding is available.
Conversation circles, online resources and drop-in ESL programs are offered by service providers, faith-based organizations, community organizations and libraries. They are another way to build your language skills and can complement formal in-class learning. Many universities also offer ESL courses that help prepare individuals for academic and professional use.
Here is a list of some Alberta schools that offer such programs.
Language Assessment
Before enrolling in a formal class, you will be required to take an assessment (test) of your English language skills, so you can be placed at the right level. This assessment is free. Your settlement agency can refer you to an assessment service or you can contact an assessment agency. Alberta Canada provides a list of language assessment and referral centre locations across Alberta. See our Find Settlement Services page for more services in your area.
Once you have completed your assessment, you will be ranked on four levels of language understanding. These areas include reading, writing, speaking and listening. These rankings will help to show your strengths and weaknesses in the English language, and help to place you in the right program. There are three phases of the Canadian Language Benchmark that you can be placed into. The first phase (CLB 1-4) shows that you have a basic understanding of the English language, and are able to communicate in common situations. The second phase (CLB 5-8) demonstrates that you have a stronger understanding of the language, showing that you can act independently in most social, educational and work related experiences. The third phase (CLB 9-12) represents an advanced understanding of the language and proves that you are capable of communicating in situation
Language Classes
Once the results of your assessment are ready, you will be able to join a formal language class.
To find language training in your area, visit our Find Settlement Services page. Choose category “Language”, and click your location in the search criteria. This will give you a list of resources and contact information and links to the organization’s website. You may experience a delay in joining a formal class due to long waitlists. While you wait, you are encouraged to join an informal language group.
Childcare
If you find it hard to attend classes due to child care duties, you should look into programs that offer complementary childcare options. Some programs provide complementary childcare offerings. Others provide instruction at various times throughout the day, like programs for mothers and their children. See our Find Settlement Services page for childcare services in your area.
Online Resources
You can also learn English online. Learn English with Canadian Broadcasting Corporation is a Canadian crown corporation that serves as the national public radio and television broadcaster
Learning English with CBC
Cooperative ESL Ministries
ESL Curriculum
Conversation Circles
See your settlement agency or library for conversation circle offerings. Here are a few examples of what is available:
Edmonton Public Library English Language Programs
Conversation Cafe
Meetup, a social media platform, also hosts informal language groups which are a great way to connect with other newcomers. Join a group, here:
Meetup ESL group (Calgary)
Meetup Language Exchange (Edmonton)
Interpreters and Translation Services
If English is not your first language, there may be times when you need someone to help you communicate. Interpretation and translation services are available.
Take care choosing an interpreter. You will need to have a good deal of confidence in an interpreter as they will deal with a lot of personal information. It is important that it is the right person and they are sensitive to cultural differences, and have knowledge of refugee situations and issues. See our Find Settlement Services page for interpretation and translation services.
Other services include:
Association of Translators and Interpreters of Alberta
MCIS Languages
Keep a Positive Attitude
Do not be discouraged if you do not see results right away! Learning a new language is difficult for everyone.
One of the first steps in settling in when you come to a new country is finding appropriate and affordable accommodation. Government Assisted Refugees (GARs) are supported by the Government of Canada through the Resettlement Assistance Program (RAP). The program can last up to one year from the date of arrival in Canada and assists in finding accommodation. Privately Sponsored Refugees (PSRs) receive housing support from their sponsors while refugee claimants are not directly supported by the government. You may be placed in temporary accommodation before finding permanent accommodation.
See the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation for more information on renting and home buying for newcomers.
Renting in Alberta
Renting means entering into a formal and binding relationship between a tenant and a landlord or property owner, where tenants agree to pay them regularly for the use of their property or land. Renting is common in Canada where the cost of purchasing a home may not be affordable.
When you are renting in Alberta, there are several types of accommodation available to meet your needs. Examples include: self-contained suite, or room in a house, a suite or room in an apartment building, room in the house with the landlord (like a basement suite) house, and condominium. For any type of accommodation, landlords (owner) expect the tenant (rental) to sign a lease. A lease is a contract that specifies the term of the rental agreement such as rent, damage deposit, conditions of eviction etc. Most landlords ask tenants to sign a one year lease. The cost of rent typically increases with the size and location of the accommodation.
Family Size
Your family size may be larger than the average Canadian size. This may make finding accommodation more challenging. Your settlement agency or sponsor will help you manage this situation, and likely has dealt with this same issue before.
Rights and Responsibilities
Tenant Rights
- Personal privacy to do whatever he or she likes (as long as it is legal)
- To be safe in their rental, free of harassment, as well as having a safe living environment.
Tenant Responsibilities
- Respect the terms of the lease
- Keep the unit clean
- Respect the neighbours. For instance, by keeping noise down or not damaging their property
- Do not sub lease the property, unless an agreement has been approved by the landlord
- Pay the rent on time
- If living in a self-standing home: Shovel the walk way in the winter and mow the lawn in the summer.
See Laws for Landlords and Tenants in Alberta for more information on tenant and landlord rights.
Damage Deposit is an amount of money that the tenant must pay the landlords with the first month rent to ensure the property is returned in good condition. It should not exceed the amount of one month rent. This deposit can be returned with annual interest as long as there is no damage to the property once you move out. For more information on damage deposits, see Laws for Landlords and Tenants in Alberta – Security Deposit.
Types of Tenancy:
- Fixed-Term Tenancy – When a landlord and tenant make a fixed term agreement (six months or one year lease). Rent cannot be increased during the term.
- Periodic tenancy – Is a week to week or month to month tenancy. The law allows the landlord to increase the rent.
The landlord can only increase rent after a certain amount of time. The notice must be in writing. It must state the amount of the increase and the date when the new rent will start.
Things to Consider When Renting:
- Location is safe, and conveniently located by transit, stores, schools, and language training
- Rent is affordable, and the unit suits the family’s needs such as larger family size or access for renters with disabilities
- Appliances and fixtures work properly (fridge, stove, fire alarms)
- For shared accommodation, fire exits are clearly marked. In all accommodations, fire exists are unobstructed
- Housing exits are not usually marked, so it is your responsibility to know where they are and alternative routes to leave
- The landlord is sensitive to cultural differences
In the event of a landlord and tenant dispute, see here more information:
Discrimination – Everyone deserves to be treated equally in the area of housing. Anti-discrimination laws exist with the purpose to prevent the violation of human dignity and freedom from the imposition of disadvantage, stereotyping or social prejudice.
Video on Housing Discrimination – Barriers to Housing
Neighbours
In Canada, people are usually friendly with their neighbours, but they keep their social distance. It is important to respect your neighbours by:
- Keeping noise level down
- Watching your children
- Staying off their property
When you first move in it is a good idea to introduce yourself to neighbours on either side of you. If you have friendly neighbours, you might share a meal with them. If you trust your neighbours, you can ask them to take in mail or newspapers for you when you are away for vacation. You can offer to do the same for them if they go away on holidays.
Neighbour Harassment
What is harassment?
If you have a neighbour that is repeatedly bothering you, let them know how they are bothering you. If they are harassing you, document the incidences by writing them down, and ask for help from your landlord, and or someone you trust. If it continues, call the police. Harassment is the continued unwanted physical contact, attention, demands, jokes or insults, by one party or a group, including threats and demands. Harassment can be a form of discrimination based on your gender, religious beliefs, colour physical or mental ability, age, place of origin, family status, and sexual orientation.
How to Find Affordable Housing
The following companies assist low income family by providing affordable housing. You might qualify for subsidized house where monthly rent is 30% of your household income. Please note, that in Alberta, like the rest of Canada, social housing is limited. It is only when the RAP program ends that GARs are able to join a social housing waitlist. PSRs can apply once they have employment. When submitting your application, you will need to provide proof of your income and status. For more information, see the Government of Alberta Housing Website.
Calgary
Edmonton
Red Deer
Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
Utilities
As a renter or homeowner, you will need to manage heating and electricity of your home, as well as internet and telephone connections. See Service Alberta for information on utilities. The following companies provide these services:
- Electricity: ENMAX This company provides electricity. Toll free number in Canada; 1-877-571-7111
- Natural Gas: Direct Energy Toll free number in Canada; 1-866-374-6299 or 403-245-7222
- Phone, Cable and Internet Services: SHAW 1-888-472-2222 or 403-716-6000 OR TELUS 1-888-811-2323 or 403-310-2255
Rental Sites
If you’re searching for an apartment online, the following websites would be useful:
Kijiji
Rentfaster
Padmapper
Buying a Home – Find a Realtor
Most Canadian home buyers hire a Realtor to support the home buying process.
Calgary
Edmonton
Red Deer
Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
Health and Safety
Smoke alarms are an important part of keeping your home safe, ensure your home has working smoke alarms, and you have a fire escape plan so you know how to get out of your home safety if there is a fire. Learn more!
Fire Prevention Week: Have a Plan
Fire Safety: Using a Window as an Fire Escape Route
Fire Safety Education Video
Bed bugs are small, oval, brownish insects that live on the blood of animals or humans, and are invisible to the human eye. They are a public health concern for all homeowners and renters in Alberta. Learn more about this issue, at My Health Alberta – How to prevent bed bug infestations. If this happens to you, it won’t be forever, but you will need to act quickly to remove the bugs. Do not take clothing or furnishings off the street or from someone who has been in contact with bed bugs.
Mold is another challenge to be aware of as it has various health implications.
House/ Apartment Protection
Your home is one of the most important possessions you may have. This link will show you how to properly protect your home. The Edmonton Police Service offer advice on apartment crime prevention.
Water
In your new home, you will have access to clean drinking water. The taps in your house provide clean, treated drinking water at any time of the day. The water has been treated with chemicals that help to clean and remove bacteria that can make you ill. Most taps are able to provide hot and cold water at any time of the day. When using hot water from the taps be careful to not burn yourself, as it can come out very hot. While there are vast amount of it available for use, try to be mindful and not waste water. In the summer time, water shortages can occur that require us to control how much we use. Outdoor water restrictions may occur, and you will need to stop using water outside such as for watering your lawn. Information will be made available online, in the local media and via social media by your municipal government. Water remains safe to drink during water restrictions.
Garbage Disposal
All cities in Alberta have a waste program to help get rid of garbage you create every day. All the waste you produce everyday must be thrown out for proper treatment into a garbage can. A garbage can should have a lining on the inside in order to prevent smell and bad odour escaping. Garbage cans should also have a lid, this will help stop animals from eating the garbage and spreading harmful diseases.
In houses, garbage disposal teams from the city come to collect the garbage on a scheduled basis. It is important to know what day this is, in order for you to put your garbage out for pick up. Many people tend to have smaller garbage cans inside the house, and one large can outside that collects all the garbage for delivery. Garbage teams come, on the specific day, and collect all the garbage in the area. Then they take this garbage to a certified dump that works to break down the garbage. If you find that you have too much garbage before garbage day and need to get rid of it, you can visit a dump by yourself to get rid of the waste for a small fee. Garbage must be placed in a designated dump.
Apartments may have a garbage chute that works to transport your garbage to a centralized area for pick up. It is important to talk to your renter about how garbage pick-up works in your area. If you do not throw out your waste properly, in some cases, you can be fined. It is important to know how to deal with your waste, look below for more information regarding waste collection programs in the following cities. Littering, throwing your garbage in the street, is also unacceptable in Canada, and can result in fines. If your city is not listed below, their website should provide information on how to properly get rid of waste.
Calgary
Edmonton
Red Deer
Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
Brooks
Recycling
Canadian communities pride themselves on how environmentally friendly they are. Being environmentally friendly involves reducing your impact on the environment. Canada has been blessed with amazing landscapes, and it is everyone’s duty to ensure that they are cared for. Many communities maintain a recycling program that helps limit the amount of garbage going into a dump or landfill. These programs are operated by the city, and only allow specific items to go into them. These include cardboard, newspaper, paper, cans, and other items. Check out the links below for what city applies to you.
Calgary
Edmonton
Red Deer
Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
This government site will also help you understand the recycling system.
When you buy certain items at the store (milk cartons, soda cans, glass bottles) you pay a small fee. You can return the empty bottles and cans to a bottle depot and reclaim this fee. These bottle depots take in your old cans and bottles, and refund the fee you paid when you bought them. These items are then recycled and used for other products. For more information about what can be returned, see Bottle Depot Refunds & Container Types. For more information regarding bottle recycling, please see Recycling 101.
Being Environmentally Friendly
Lake Louise. Photo by Julia-Maria Becker
Alberta prides itself on its outstanding natural beauty. The Rocky Mountains, plains and other natural features help make this province what it is. It is important then to understand how our everyday living effects the environment, and to take into consideration what are actions mean for the environment around us. Climate change is a serious issue facing the world. It occurs when long-term weather patterns are altered — for example, through human activity. This is leading to an increase in the average global temperature which is causing rising sea levels, and the occurrence of more frequent and severe natural disasters all over the world. Climate change needs everyone’s attention because it affects everyone. Recycling programs help to limit the damages on the environment. Other strategies include alternative modes of transportation (like walking, busing, biking). For more information on how you can do your part, see Alberta Government – What you can do.
Furnishing
Most rental properties do not come with household furnishings. If you are a GAR, your settlement agency may provide you with basic furnishings. If you are a PSR, your sponsor will help you prepare your home. Many organizations in Alberta collect and support Albertans with donated clothes, furnishing and beds.
Women in Need
Goodwill
Interfaithfurniture
Salvation Army
Value Village
Kijiji
Home and Property Insurance
You will need to take out insurance on your home whether you are renting or an owner. Insurance is an agreement between an individual and a company where the individual pays regular payments to a company and company agrees to pay money if the person’s house or property is damaged, lost or stolen. Some leases require renters to have insurance.
See this link for information on how to purchase home insurance.
Home and Property Insurance
Short-Term and Emergency Housing
Initially, you may need to live in short-term housing. This includes hostels, hotels, and shelters. If you find yourself in need of safe, affordable housing, such as when experiencing a personal crisis like domestic violence, a sudden urgent or unexpected occurrence or an occasion requiring immediate action like a flood or fire, these may also be options for you until you can find permanent housing again.
Homelessness
Homelessness describes the situation of an individual or family without permanent and appropriate housing, or the immediate, ability of to gain for oneself. In the case you find yourself in this situation, it is important to know that services are available to help provide a safe space for whatever situation you are in.
Areas like Calgary, and Edmonton have dedicated homeless shelters that offer emergency beds and food services for those who are in an emergency, and cannot access suitable housing or food services. Areas in Red Deer and Medicine Hat offer temporary accommodations for individuals as well. See here to Find a Shelter in locations across Alberta.
Women’s Shelters
If, as a woman, you feel unsafe physically, emotionally, and mentally it is important to know that services are available to help you. Many women shelters exist in Alberta that work to create a safe space for women who are escaping violence and abuse. A women’s shelter is an environment that helps women escape from domestic and intimate violence, be it physical or emotional.
This interactive map provides locations of women shelters in Calgary, Edmonton, and the rest of Alberta. See Shelter Safe to find a women’s shelter near you.
Employment is how people earn an income and financially support themselves. There are various types of employment such as full time, part-time, contract, casual or seasonal employment. This section explores the steps in finding a job, Canadian employment law and rights, employment programming information, and tips for success.
Working in Your First Year in Canada
The Resettlement Assistance Program (RAP) provides income support from the government for up to 12 months for Government-Assisted Refugees (GARs). While under government assistance, GARs are also able to earn up to 50% of their RAP income support before any deduction are made to this income support. Once the income for the individual or family is greater than 50% of their RAP income, the RAP support is reduced on a dollar-for-dollar basis.
Employment Programming
Once you are ready to start looking for a job, there are supporting services to help you find a job and prepare you for employment. Organizations such as settlement agencies may provide support in helping you find a job. These services may include advice on resume building and job interview preparation, as well as finding opportunities for internship and volunteer positions. Your settlement agency will also help by setting you up with an employment counsellor.
Employment and Career Resources
Working in Alberta
Finding Employment – Employment services are available to help you get a job! Check out our Find Settlement Services page for employment services near you.
Finding a Job
When applying for a job, it is it is normal for employers to request a resume, and cover letter. A resume or Curriculum Vitae is a short description of your professional or work experience and qualifications. A cover letter tells an employer how your experience relates to the job posting, and why you are interested and qualified for the job.
Be sure to include your name, address and contact number on both documents so that an employer may contact you. Ensure your voicemail is set up on your phone so that you can be contacted by a potential employer.
Most applications are made online by email or through a job site. To find work, you will need references; these are generally previous employers who can speak to your work skills. Connect with your references, and make sure they know you are using them as a reference. The most important advice when seeking employment is to stay positive. Finding employment is not easy.
For a guide on writing your resume, please consult:
How to write a Canadian-style resume
How do I create a Canadian-style résumé in order to find a job?
Social Insurance Number (SIN)
To work in Canada and receive government benefits, you need a Social Insurance Number.
It is a 9-digit number which identifies people who earn money, pay taxes, contribute to pension plans, and use government services. It is best to apply for your SIN as soon as possible. An employer is not legally able to pay you if you do not have a SIN, and they must ask for your SIN within 3 days of starting your job.
Services for Youth: Social Insurance Number
The Job Search
Once you have your resume prepared, it is time to start looking for a job. There are a number of ways to find employment. They include:
Finding jobs on internet sites: Look for jobs in Alberta, Alberta student and youth jobs
“Help Wanted” notices in local stores, malls and shops
Volunteering is a great way to gain experience in Canada, build new skills, contribute to your community, and meet new people: Volunteer Alberta
Through talking to friends, acquaintances and professional contacts acquaintances (Networking). See this video: The Job Search: Networking for Newcomers
Career Fairs – Look for job fairs in your community to meet employers who are hiring. To learn about job and career fairs: Alberta Job & Career Fairs
Classified ads in the newspaper
Calgary
Find jobs with Calgary Herald & Workopolis
Edmonton
Find jobs with Edmonton Journal & Workopolis
Red Deer
Find jobs in Central Alberta
Lethbridge
Find jobs with Lethbridge Herald
Medicine Hat
Find jobs with Medicine Hat News
For more information: Look for jobs in Canada
The Interview
After successfully applying for a job, you are likely to be contacted for an interview where you will be asked in come in for a brief in-person meeting to discuss your previous experience and how it makes you suitable for the position. It is recommended that you give examples of past work experiences of how you solved problems when you answer their questions. It is important to talk about yourself and how you are capable. Other tips include:
- Make eye contact with your interviewer
- Be at least 5 minutes early for the interview
- Dress presentably in clean, un-creased clothing
Canadian Work Experience
Employers also look for Canadian work experience and certification. Initially you may be required to take a job that may not be your first choice. It is important to keep in mind that Alberta employers typically look for strong English language skills so your language classes are important. There are still opportunities to find employment without strong English language skills, but learning the language will be very beneficial for future job applications.
The Government of Canada offers a Federal Internship program for newcomers: Apply for the Federal Internship for Newcomers Program
Foreign Credential Recognition
Would you like to work in your trained profession or trade?
It may be difficult for some employers in Canada to recognize qualifications attained in a foreign country. Also, many skilled professions require a Canadian issued license or permit to work professionally. There are many services available to have your foreign qualifications, education and licenses recognized and assessed. Foreign credential services are available, here:
CIC Foreign Credentials Referral Office
International Qualifications Assessment Service (IQAS)
Assessments and recognition can also be arranged by your employment counselor. See also: Educational Credential Assessment for Immigration Purposes
It may be difficult to immediately find a job in your profession or trade. Keep in mind some qualifications are not transferable and you may need to upgrade your qualifications to certain standards in Canada.
Newcomers in Alberta: Work Experience and Credential Recognition
Women in the Workforce
Many women work in Canada. Employment programs exist for women to support them with their successful job search. These services range from career planning, interview preparation, networking and many others.
Calgary CIWA Employment Skills Program
Edmonton Pre-employment Training Program
If you live outside of these centres, your settlement agency may offer programming for women.
Financial Support
The Government of Alberta also helps newcomers by providing financial support and training: Alberta Human Services Full-time training
Employment Insurance
If you lose your job, you may be eligible for Employment Insurance (EI). EI provides temporary benefits for individuals who have lost their job through no fault of their own. You should apply for EI benefits as soon as you stop working, to make sure you receive all the benefits available to you.
Applying for Employment Insurance benefits
Employment Insurance benefits
Workplace Advice
Workplace Culture
Workplace culture may be different your home country. Some examples include:
- Questions are encouraged
- Punctuality is very important
- Clear communication highly valued. I.e. make sure your employer knows if you are sick, and won’t make it to work
- Avoid gossip
- Be friendly but professional with coworkers
- Be confident
- Be respectful of your coworkers and the workspace
- Racial, Sexual or discriminatory comments or acts are NOT appropriate at the work place and may be due cause for dismissal
- Keep your workplace neat and tidy
- Avoid asking others how much money they make
For more information, see:
Newcomers in Alberta: Work Culture
What is “Workplace Culture”?
Expectations in the Canadian Workplace
Workplace Safety and Your Rights
Alberta has laws to ensure the safety of employees in the workplace. The majority of industries are provincially regulated while others are regulated by the federal government. A supervisor is responsible for making sure workers are working safety, and knowing about hazards, and anything that hurt them at work. Employees have the right to refuse dangerous work, and cannot be fired for doing so. They have the right to be properly trained to do their job safety. There may be occasions where you notice workplace hazards or safety concerns not noticed by your supervisor. If you see something dangerous in the workplace, you should tell your supervisor immediately.
As an employee you are responsible for following safety protocols at work like wearing safety gear, and taking the safety training.
Labour Program: Health and Safety
Work Safe Alberta
You can report unsafe conditions at the workplace online, or by calling the Occupational Health and Safety line.
If you work in a federally regulated workplace, you must first attempt to resolve your complaint as part of an internal resolution process. Only then, can you file a complaint with a Health and Safety Officer.
Discrimination and Harassment
As an employee, you are also protected by law against discrimination and harassment including based on race, gender, and religion.
As defined by the Canadian Human Rights Commission, “Discrimination is an action or a decision that treats a person or a group negatively for reasons such as their race, age or disability”. As for harassment, it is “a form of discrimination. It involves any unwanted physical or verbal behaviour that offends or humiliates you. Generally, harassment is a behaviour that persists over time. Serious one-time incidents can also sometimes be considered harassment.”
Sexual harassment is, “any conduct, comment, gesture, or contact of a sexual nature that is likely to cause offence or humiliation to any employee; or that might, on reasonable grounds, be perceived by that employee as placing a condition of a sexual nature on employment or on any opportunity for training or promotion.”(Canada Labour Code).
For more information on what bullying, and sexual harassment looks like, see:
- Stop Sexual Violence
- Workplace Bullying
For more information, please visit the Canadian Human Rights Commission.
- Know Your Employment Rights
Holidays
There are nine statutory holidays in Alberta. You may be eligible for holiday pay. General Holidays and General Holiday Pay
Start Your Own Business
You could be part of the 20% of newcomers who start their business in Canada. To do so, you will need to build a credit history in Canada. For advice about starting your own business:
Resources for starting a business
Start your business
Related Articles
What Newcomers Need To Know About Entering Canada’s Workforce
Federal labour standards and Alberta labour standards provides information on aspects such as wages, pay and deductions, termination and layoffs, and employer compliance: Federal Labour Standards and Alberta Employment Standards
Useful information on employment contracts:
What you need to know about employment contracts
What Newcomers Need To Know About Entering Canada’s Workforce
Advice for Syrian refugees arriving to Canada
For Parents
Throughout Alberta, childcare programs exist to support parents while settlement agencies as well as many other non-profit and community organizations provide fun programming for children and youth. According to the Government of Canada, a child is defined as a person 14 years and under, while a youth is generally a person aged between 15 and 30. This section provides an overview of available programming, and discusses challenges around growing up in two cultures.
Childcare
In Canada it is common to use childcare centres for others to look after your children while you are at work. Childcare workers will respect your child rearing practices on food, sleep, habits and any other concerns or traditions you may have.
Information on Childcare in Alberta
Canada Child Benefit
There are many support services provided to help parents with the cost of raising children under 18 years of age. This includes the Canada Child Benefit (CCB) which is a tax-free, monthly payment from Canada Revenue Agency to those families eligible.
Information on childcare and how to apply for financial support can be found at: Canada Child Benefit
Child Support Services
There is a free service via Alberta Works to provide help to parents with limited incomes to get child support agreements or court orders. Next to earned income, child support has the biggest financial impact for families with limited income. Child support continues until the child is at least 18 years of age. More information on receiving child support can be found at: Child Support Services
For Youth
Find a Mentor
A mentor is a trusted guide and advisor. A mentor can share important cultural experiences and community connections with young people. Find a mentor to help you grow and stay on track, here:
Alberta Mentorship Partnership
If you need someone to talk to, do not hesitate to reach out to someone you trust!
Brotalk: A support zone for teen guys.
Kids Help Phone: every call is an act of courage (1-800-668-6868)
Use our Find Settlement Services page to find youth services in your area
Find a youth program near you
Looking for something fun to do? Want to build your skills, and meet new people? For more resources, see below.
Calgary:
Find Settlement Services in your area.
The Calgary Youth Services Guide provides useful information with regards to available services for youth. Such services include finding a job via the Youth Employment Centre, accessing counselling services, libraries and recreational centres. Communities throughout Calgary (such as Bowness in the NW, Falconridge and Pineridge in the NE, Penbrooke in the SE, and Shawnessy in the SW) provide arts, fitness, and recreational facilities.
Services Specific to Newcomers
There are specific services for newcomers to help them integrate into Canadian life through sports, debate teams, leadership programs, networking events to meet new friends, and events to learn about Canadian culture.
New Canadian Friendship Centre holds various events for newcomers to Canada to meet others like themselves, share stories, learn new skills, and learn about Canadian customs and culture, as well as each other’s.
Youth Inclusive Neighborhoods Project allows youth aged 13-16 to attend “workshops, meet and connect with other teens, participate in sports, go on field trips, volunteer in community action projects and be parented with a mentor.”
Calgary Bridge Foundation offers an inclusive environment for immigrant and refugee youth and their families by providing information, knowledge and experience for their new lives in Canada. The programs offered focus on building knowledge of Canadian and Calgarian culture, integration within local communities, improved English language skills, development of personal, social and leadership skills and successful graduation from school. Information on events held by CBFY can be found at: CBFY Events
Boys and Girls Clubs of Calgary offer programs to children and youth that support the healthy physical, educational and social development of young people and their families. There are over 40 programs at countless locations in Calgary, information on these programs can be found at: Boys and Girls Clubs of Calgary Programs
Arts
Many communities provide activities to youth. These activities include drawing, painting murals, playing music, and participating in video projects. The Antyx Community Arts Society provides such activities to 13-18 years old youth.
Other programs can help young people deal with personal conflicts, missing school, sexual violence and/or abuse:
Calgary Police Services offers youth aged 12-18 with free interactive workshops. The aim of these workshops is to help youth interact with police figures and avoid conflicts. School Resource Officers guide youth involved in drugs, crimes, gangs and peer pressure.
Stoked at Staying in School, a financed 9-week program that seeks to help youth aged 15-18 who are not attending school.
Start Smart Stay Safe, a program which seeks to help youth deal with bullying, cyber-safety and peer pressure.
Crisis Intervention seeks to help survivors of sexual abuse. The program provides counselling and crisis intervention.
Eastside Family Centre is another free walk in program which seeks to provide counselling services.
Bridging the Gap is a program for youth suffering from mental illness.
ReDirect is a program provided by the Calgary Police Services which “is a prevention and education program aimed at youth and young adults vulnerable to becoming radicalized, before they develop extremist ideologies or intentions.”
Edmonton:
Find Settlement Services in your area.
The City of Edmonton provides many programs for youth, which includes the 124 Youth Program, Leaders in Training, and Rising Youth. These programs help young people make friends. They are recreational as well as educating.
Rising Youth Program is a source of fun activities for youth in the community. The program is free and is open to youth from Grade 9 to Grade 12. Outings include rock climbing, biking, swimming, and hiking.
Leaders in Training is for youth aged 13-17 and runs from May until August. The program allows youth to be volunteer recreation leaders. Youth participate in crafts, drama, music and sports.
124 Street Youth Drop-In Program accepts youth aged 12 to 17. The program is held evenings and weekends.
Red Deer:
Find Settlement Services in your area.
Youth Employment Services (YES) assists youth in their quest to find employment.
The Boys and Girls Club of Red Deer and District holds its events in the Youth and Volunteer Centre of Red Deer.
Red Deer College offers summer camps for students interested in film design, game design, sports, dance, music and the visual arts.
Tree House Youth Theatre produces musicals. The theatre “offers a place to learn skills and get together as a community”. For more information see What is the Tree House Youth Theatre?.
Cornerstone Youth Theatre is another initiative to involve youth in the arts. It provides after-school classes and summer camps. It also makes musical productions.
Welcoming & Inclusive Communities Network (WIC) holds community conversations to reduce racism and discrimination. WIC welcomes all individuals, regardless of their faith, gender, or sexual orientation.
Youth aged 13-21 facing addiction, sexual exploitation, and mental illness can attend the Street Ties Outreach Program, which is part of the Vantage Community Services.
The Red Deer Soccer Association seeks to involve youth in sports.
Lethbridge:
Find Settlement Services in your area.
Youth HUB is the go-to place in Lethbridge. It “assists youth to access resources to secure housing, navigate and connect to community systems and provide supports and advocacy that allow youth to fully participate in community life.”
For sports, there are many sport and recreation organizations in Lethbridge. Among them, are the Lethbridge Hockey Club and the Lethbridge Curling Club. Hockey and curling are two very popular sports in Canada.
Ascent Climbing Centre is located at the University of Lethbridge for anyone interested in rock climbing.
Allied Arts Council of Lethbridge is in Lethbridge if are interested in the arts. There is also the Lethbridge Highland Dance Association and the Lethbridge Musical Theatre. The Lethbridge Musical Theatre is now accepting submissions for its fall performance.
Medicine Hat:
Find Settlement Services in your area.
Medicine Hat Youth Action Society is in Medicine Hat for youth. This organization “seeks to improve the physical, social, mental, emotional, spiritual and cultural reality of youth in Medicine Hat and surrounding area.” It celebrates Youth Day, held on August 15th of every year. Its Blue Ribbon Initiative helps youth perform random acts of kindness.
Med Hat Active also provides activities for people of all ages. These activities include disc and wheel sports, fitness, water sports, martial arts, and arts.
Youth Hub is also in Medicine Hat. The hub offers free services such as mental wellness, housing and financial support to youth aged 13-24.
YMCA Employment Centre is can help you find work.
Medicine Hat Soccer Association has outdoor and indoor soccer.
For more activities in Red Deer, please consult the Red Deer City Guide. The guide provides programs in arts and culture, aquatics, clubs, fitness and wellness, as well as sports.
Brooks:
Find Settlement Services in your area.
Brooks & County Immigration Services connect young newcomers to the community. Their services include: youth support; connecting youth with volunteering opportunities; explaining how to obtain a driver’s license; helping youth find out about career opportunities and how to obtain a job; and providing study help. More information can be found on their website.
Ashton Place Youth Center has for mission “to develop the academic, intellectual, emotional, physical, employment, and social competence through semi-structured programs.”
Fun Fact: Students from Grade 7 until Grade 9 have a free pass to the Brooks recreational facilities. The Youth Activation Pass is valid all year long.
SPEC Association for Children & Families offers programs and services for children and families with a focus on positive development of kids by providing services from early intervention (prevention) to high intervention during crisis. SPEC continues to focus on preventive and educational programs that promote caring and committed communities where children are valued.
Growing Up in Two Cultures – Cultural Identity
Canada is a multicultural country. Despite living in a multicultural country, many immigrants face language and cultural barriers. When you move away from your culture, and into another one, you may experience some challenges that come with adjusting to a new way of life. The struggle to adjust to Canadian society is normal. For example, being in school can be difficult for newcomers because they may not know many other people yet and need to learn English. Being able to embrace one’s dual nationality is important and takes time.
Youth integrating into Canadian life can run into challenges with family as they take on aspects of Canadian culture that are different from their original culture such as clothing. Culture can be complicated, and in a multicultural family there are many different aspects that can affect relationships.
Some the issues that can be difficult with a parent from a different culture are:
- Language barriers with your parents
- Feeling stuck between two cultures
- Feeling different to your friends and classmates
- Experiencing discrimination and distancing yourself from your parent’s culture to avoid it
- Different opinions on things like dating, alcohol and curfews
- Dealing with the responsibility of helping your parents adjust to the new culture
To read stories about youth, like you, growing up in two cultures, see:
Children of immigrants caught between 2 cultures
The New Citizens
Conflict between family and culture in Australia
Raising a Canadian: immigrant children develop different views
Culture differences between generations
You and the Law
The legal age to drink and smoke in Alberta is 18. Drinking is regulated by the Alberta Gaming and Liquor Commission.
Smoking is bad for your health. Smoking is forbidden inside cafes and restaurants. Smoking is regulated by the Tobacco and Smoking Reduction Act.
Fun Fact:
Youth Quidditch exists! The sport even exists in winter! For a list of locations, please visit: Central Alberta Quidditch
Welcome to Your New Home!
Welcome to Canada and Alberta, we’re happy that you are here with us!
To help you have the best possible start to your new life in Canada, this page will offer you helpful information and various tips for all the exciting things you can expect from your new community. Information found below includes places of worship, libraries, sports, ethno-cultural associations, festivals, and programs for the LGBTQ community and women.
Firstly, here is a welcome message from Canadian kids. Coming to a new country may be daunting, but you are not alone.
Many others have come to Canada to start their new life, and are facing a similar situation. In December of 2015, Emad and his family left their home in Syria for a safer life in Ontario, Canada. Day by day, they are growing accustomed to a new home, country and language. This is just a small glimpse of their story.
Your Community
There are many ways to connect with your community, and help build your new life in Canada. Reaching out to your neighbours is one way you can do this. Canadians are proud of their multi-cultural heritage and will be glad to hear your story.
One of the first stops on your resettlement journey is to visit a settlement agency where there are a lot of opportunities to connect with others. Settlement agencies are organizations that provide settlement services such as: interpretation, help with forms and applications, English as a second language classes, help in finding a job or training, and information about other community services. Find Settlement Services in your area.
Beyond that, you can participate with community centres that offer different types of activities to enjoy. Do you like sports? Knitting? There is a program for everyone! Below we will discuss aspects of community in Alberta such as ethno-cultural groups, religious and public institutions, sports facilities, community organizations and centres.
If you ever need help finding a service, like parenting and family programs or mental health assistance, you can phone 211 to speak to a person who can connect you to thousands of community, social and government resources 24/7. You can also search the 211 Alberta online resource directories.
Places of Worship
Alongside the private practice of religion, Canadians show their religious faith in public and in their daily activities. They also gather in:
- Churches
- Mosques
- Synagogues
- Temples
- And other places of worship
Public Libraries
Calgary
There are 18 public libraries in Calgary. They are for the most part open every day except, with some exceptions on Sundays. See here for a list of libraries and hours of operation.
Edmonton
There are 22 public libraries in Edmonton. See here for a list of libraries and hours of operation
Red Deer
There are three public libraries in Red Deer. See here for a list of libraries and hours of operation.
Lethbridge
There are three public libraries in Red Deer. See here for a list of libraries and hours of operation.
Medicine Hat
There is one public library in Medicine Hat. See here for more information on Medicine Hat’s Public Library.
Brooks
There is one public library in Brooks. See here for more information on Brooks’ Public Library.
YMCAs
Eight YMCAs and seven YWCAs can be found throughout Calgary. They provide health and wellness programs for children, youth and adults, as well as services for newcomers.
The YWCA is focused on programming for women. The YWCA has a 24 hour crisis line and housing programs for women.
Community/Multi-cultural Centres, and Resources
Calgary
There are 128 community centres in Calgary, which are used for events, programs, and meetings. Many community centres are also child care and sporting venues.
Calgary Community Associations
In some cases, accessing these lower income services can be difficult. The City of Calgary provides Programs and services for low income Calgarians.
The Calgary community has many interesting events and opportunities to offer new families. See Life in Calgary for more information on things to do in Calgary.
Many centres in Calgary offer facilities to participate in physical activity. These could include gyms, pools, skate parks, ski hills, mountain biking and so on. The City of Calgary offers a range of activities and recreations through Calgary Recreation.
The University of Calgary’s website provides a list of Multicultural Centres and Resources in Calgary.
Edmonton
Edmonton also has many community centres. The City of Edmonton provides a list of Community Recreation Centres, Leisure Centres and Pools.
Others include the following:
- Canadian Arab Friendship Association
- Canadian Hungarian Cultural Society of Edmonton
- Canadian Islamic Centre & Al-Rashid Mosque
- Canadian Romanian Society
- Dutch Canadian Club
- Filipino Canadian Women’s Barangay Association
- Multicultural Health Brokers Co-operative
- Somali Canadian Cultural Society of Edmonton
- Slovenian Canadian Association
- Terwillegar Community Rec Centre
- Ukrainian Youth Association
- Chinese Benevolent Association of Edmonton
- Nigerian Canadian Association of Edmonton
- Pakistan Canada Association Edmonton
- Edmonton Afgan Charitable Association
- Somali Canadian Cultural Society of Edmonton
- Iraqi Canadian Association of Canada
Red Deer
The City of Red Deer has 18 Neighborhood Activity Centres. These centres can be used for yoga classes, family activities/reunions, and get-togethers.
For a wider range of recreational activities, you can attend the Rotary Recreation Park. It has drop-in schedules for swimming and exercise.
Lethbridge
Lethbridge Things To Do
Lethbridge maintains numerous clubs and associations where members can gather to share ideas and thoughts. Find Lethbridge Clubs & Associations In Your Area.
Medicine Hat
Medicine Hat Cultural Centre
Medicine Hat features several recreational facilities where individuals and families can gather and engage. Find a Recreation Centre near you.
Sports and Exercise
There are a range of organized recreational options in your community such as friendly leagues where everyone can participate no matter their skill level and experience. There are a wide range of different leagues such as: soccer, tennis, badminton, basketball, volleyball, hockey, and many others. Some leagues are more competitive, and require greater skill levels to participate. When joining, try to find a friendly league to get you introduced to the activity. Also, recreational centers within each city have indoor pools and waterslides for everyone to enjoy.
Calgary
The Calgary Sport and Social Club offer over 15 sports with an emphasis on “fun-first, winning second”. There are also parties and events offered throughout the year. As examples, Sportball has been encouraging kids to “play with passion, play for fun” since 1995. KidSport™ welcomes all new applications and donations so that you can be a part of their team.
Edmonton
In Edmonton, Edmonton Sport and Social Club is the City’s #1 Co-ed Adult Sports Provider. Sports For Kids, which is a physically active childcare program, provides children with opportunities to experience a variety of different sport and recreational activities.
Red Deer
The City of Red Deer offers recreational activities in four locations. One of its programs, Swim Kids, is for children ages 6+. Its recreational facilities offer dropping classes for fitness, skating or swimming, climbing, and racket sports.
Lethbridge
The Lethbridge Sport Council has many programs for kids of all ages. City of Lethbridge Leisure also provides recreational activities. The activities will be provided in a safe, open, and enjoyable atmosphere, where sportsmanship, participation and fun will be encouraged at all times.
Medicine Hat
The Alberta Marlin’s Swim Club is located in Medicine Hat. It offers kids of all ages the opportunity to learn how to swim and improve upon their skills. The Crestwood Recreation Centre has a six-lane 25m pool and a racquet court.
Summer
During summer months, residents can enjoy parks and school grounds to play basketball, soccer, and Frisbee. You can also go hiking in the mountains. National Parks Canada offers a list of hiking trails for sight seekers.
National Parks
Canada will celebrate its 150th birthday in 2017 and the Government of Canada has announced free admission for all Canadian and international visitors to Parks Canada this year.
This is Canada’s birthday gift for all to enjoy and explore the national parks, historic sites and national marine conservation areas which are operated by Parks Canada. Five of these sites are considered World Heritage Sites by UNESCO.
Below you can find links to a number of beautiful and historical sites across Alberta, some of which are national parks:
- Head-Smashed in Buffalo Jump – World Heritage Site – For nearly 6000 years, the jump was the location where indigenous people hunted bison.
- Dinosaur Provincial Park – A World Heritage Site in 1979, the site has dinosaur and fossil exhibits. The park protects prairie grasslands, badlands, and riverside cottonwoods.
- Drumheller Valley – Drumheller is also known for its badlands and dinosaur displays. Drumheller is close to Calgary, Banff, and Red Deer.
- The Canadian Rocky Mountain Parks – World Heritage Site since 1984. Some of its parks include Banff and Jasper. Visiting Lake Louise is also a must. The scenery will leave you speechless. You can walk and follow hiking trails.
- Waterton Glacier International Peace Park– Created in 1932 and a World Heritage Site since 1995. It joins the Waterton Lakes National Park in Canada and the Glacier National Park in the United States.
- Wood Buffalo National Park – This World Heritage Site since 1983 protects the bison within 44 807 square kilometers.
- Travel Alberta is another great resource for must-see destinations.
Other resources include:
Summer in Alberta
Remember to Breath – Travel Alberta
Winter
Within Alberta there is a wide selection of winter activities both in the Canadian Rockies, and also throughout cities and communities with public skating rinks. Skiing, snowboarding and skating are a huge part of Canadian national culture, there are many opportunities to learn and take lessons for both children and adults alike across Alberta. In fact, Calgary was the host of the 1988 Winter Olympics.
Skiing and Skating
There are many public outdoor skating rinks throughout Alberta.
- Calgary’s main ice rinks are Olympic Plaza, Prairies Winds Park and Bowness Park Lagoon.
- Edmonton also has various rinks located across the city such as at City Hall, Castle Downs, and Victoria Park.
- Red Deer offers 62 outdoor rinks. Some of these rinks, such as Bower Place and Clearview Meadows, have indoor shelters.
- Lethbridge has three designated skating areas. These are Chinook Lake, Nicholas Sheran Lake and Henderson Lake.
- Medicine Hat residents can Adopt-a-Rink to maintain rinks such as the Jefferies Rink and the East Glen Rink, throughout the season. Various private facilities offer skiing and skating lessons during the winter months.
- Brooks has two rinks maintained throughout the week only. These rinks are located in Griffin Park and Rose Lea Park.
The following are a number of examples of ski parks that accommodate a variety of skill-levels:
- Winsport is situated in North West Calgary, just off highway. This Olympic-based facility offers skiing, skating and many other activities.
- Nakiska Winter Snow School is also known as “Calgary’s Learning Mountain! This is just a short 45 minute drive away from Calgary.
- Lake Louise is consistently voted as one of the world’s best ski resorts, with breathtaking views and some of the best skiing in the Canadian Rockies. Lake Louise is situated in Banff National Park, a two-hour hour drive from Calgary. The Lake Louise Ski Resort provides ski lessons and rentals.
- Another family friendly ski resort is Sunshine Village, situated just over an hour away from Calgary, just outside the town of Banff.
- Norquay Ski Resort is another family friendly ski area that is ideal for learning and also has a family tube park.
- Canyon Ski Resort is located in Red Deer, with 70 acres of skiable terrain, 18 runs and 6 lifts.
- Located in Edmonton, Rabbit Hill is great for beginners and children.
General Events Calendars
Below you will find general event calendars for different locations across Alberta. Be sure to keep a look out for upcoming events and activities, these websites are updated frequently!
- Coming up Calgary
- Southern Alberta Events
- Edmonton Events Calendar
Festivals
Alberta is a vibrant province with activities for people of all ages, cultures and interests. There are many festivals across Alberta, some of these are free. You can attend and even be involved in a wide array of festivities.
Calgary
- Calgary Stampede is an annual exhibition, rodeo and festival held every year early in July in Calgary, Alberta. The Stampede is a ten-day event, which features one of the world’s biggest rodeos, chuck wagon racing, a free parade, rides, games, midway, stage shows, live music concerts, agricultural competitions, animal barns, First Nations exhibitions, and free pancake breakfasts.
- Calgary Folk Fest Festival: This amazing festival brings instrumentalists from all over the world. There is also music, dancing, and a beer garden.
- Canmore Folk Festival: is the longest running folk music festival in Alberta and one of its finest. Adhering to a philosophy and legacy of folk, world, blues and roots music, the festival since 1978 has attracted up to 21,000 music fans annually from across southern Alberta, western Canada, the northwestern USA and indeed the world.
For more information about events in Calgary, see the Coming up Calgary – Events Calendar. You can search for music, art, and community events that are happening in and around Calgary based off what your preferences are.
Edmonton
- Taste of Edmonton: This festival is outdoors and has food and entertainment.
- Edmonton Blues Festival: Join the crowd at this three-day festival in August.
- Edmonton International Jazz Festival: The festival has educational program and critically-acclaimed artists.
- K days: is Edmonton’s biggest summer festival
Lethbridge
- Lethbridge Jazz Festival: This jazz festival is outside. It has beer gardens and many vendors.
Medicine Hat
- Medicine Hat JazzFest: This festival celebrated its 20th anniversary this year.
Support for Women
There are lots of places to connect as a woman in the community, to get help and/or make a difference.
The Royal Women Association video shows why community is so important for women.
Below is a list of support services for women in Alberta:
Calgary
- Women’s Centre of Calgary
- I am a woman: The Women’s Centre of Calgary
- Calgary Immigrant Women’s Association (CIWA)
Edmonton
- City of Edmonton – Women’s Support Services
- Changing Together is a support centre for immigrant women in Edmonton.
Red Deer
- Central Alberta Immigrant Women’s Association (CAIWA)
- Women’s Outreach
Lethbridge
- Women Space
If you are in an abusive relationship, the Calgary Women’s Shelter has a free 24/7 helpline at 403.234.7233 (SAFE). Trained counsellors will help provide counselling and safe solutions in your language.
For men: The Calgary Counselling Centre has a Male Domestic Abuse Outreach Program.
For a list of common examples of abusive behaviour, please consult Forms of Abuse:
Alberta Council of Women’s Shelters
LGBTQ+ Community
Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer people and other related communities (LGBTQ+) have a right to equality, and there are many safe spaces to connect with others in the community. LGBTQ+ communities have access a number of online programs and supports that address many of the issues they may face. The following is a list of many of these safe spaces:
Calgary
- Calgary Outlink Calgary Pride is a 31-year old community hub.
Edmonton
- Pride Centre of Edmonton Trans Youth Camp is held in August. The Pride Center is wheelchair accessible.
- Youth Safe (AGAPE) – A focus group at the Faculty of Education of the University of Alberta.
Red Deer
- Meetup – On this site you can find many dates of Meetups. There are currently 202 members of the Red Deer/ Central Alberta LGBT Meetup group.
- Red Deer Pride Days are in August. The first event was in 2013.
Lethbridge
- The Outreach Southern Alberta Society provides education and resources. Meetings are twice a month.
- Gay Lethbridge
- Lethbridge Pride Fest is a day of celebration held in June.
- PFLAG Canada supports, educates and provides resources to all individuals with questions or concerns about the LGBTQ community of Canada. See The Big Gay Hindu Wedding.
Medicine Hat
- Medicine Hat Pride This year, the Medicine Hat Pride has an AIDS Benefit and a fashion show.
Youth
- Youth Safe.net is a guide to Alberta’s resources for youth
- Gay-Straight Alliances in Schools
- Government of Alberta – LGBTQ support
Food Banks
A food bank is an institution where individuals and families in need can access basic food items for survival. If you or your family are in immediate need for food, there are foods banks across Alberta to help. For more information please see the following:
- Alberta Food Banks
New financial skills may be required in your new life in Canada like understanding the Canadian financial system. While this can be challenging to learn, this section makes it easier for you providing information on the Canadian currency, banking in Canada, taxes (taxes are collected by the government so that they can offer public services such as health care), and tips on how to manage your finances well.
Financial Literacy and Training
Financial literacy is having the knowledge, skills and confidence to make responsible financial decisions. Resettlement Assistance Program (RAP) providers may offer financial training when you first arrive that covers basic information and support such as setting up a bank account. Sponsorship Agreement Holders (SAHs) may provide similar support to Privately Sponsored Refugees (PSRs).
It is recommended that you continue to increase your financial literacy. Some multicultural groups and settlement agencies offer financial counselling in specific languages.
Understanding Your Pay
Canadian Currency
In Canada, we use coins and bills called cash. Cash should never be sent by mail. Other payment methods include: debit cards, cheques, and credit cards.
First Steps – Set Up a Bank Account
It is recommended that you set up a bank account, and get a bank card right away. Banks require two pieces of ID (landing document and a passport are acceptable). Call ahead if you can to find out information about what documents you will need present to the bank to set up an account. Some major banks offer a newcomers package with advantages such as getting a credit card with no deposit or credit history, and no monthly fee on your bank account for a limited time.
Overall, the benefits of having a bank account include safety, affordability, and accessibility (for example, employers are able to deposit your salary directly to your account). For more detailed information about banking for newcomers to Canada, here.
There are two basic types of bank account:
- Chequing account (banking or transaction account)
- Saving account
How a Chequing Account Works
With a chequing account, you can deposit and withdraw money from an Automated Teller Machine (ATM) or bank tellers with a debit card. Also, keep in mind that most banks charge a monthly fee (approximately $10.00) for your account. It is possible set up a joint account: a bank account shared by two or more people (e.g. open one with your spouse). If you are interested in starting a small business, see the Canadian Bankers Association – Small Business Services for more information.
How Debit Cards (Bank Client Card) Work
Automated Teller Machine (ATM) or cash machines are accessed by using your debit card and Personal Identification Number (PIN). Your account can be accessed anywhere in Canada and other countries. Debit cards provide convenient and secure access to your money. You are able to deposit and withdraw money at any ATM and to make direct payments. Keep in mind there are daily withdrawal limits. There is a service fee to use an ATM which can range from 2 – 3 dollars. To access your account, a confidential PIN is required. It is usually four digits long that you select (i.e. 1234). Remember to protect your PIN each time, by covering the numbers with your hands, and body. Do not share your PIN with anyone. If you suspect that someone knows your PIN, change it immediately.
How to use an ATM?
Cheques
Cheques are commonly used to pay the rent and bills although you can also pay your bills online through e-banking. They have the account number of the owner and must be signed. You can order a book of cheques from your bank. Please ensure you have enough money in your bank account to cover the amount of the cheque or you will receive a fee. When deposited, cheques can be put on hold for few days (4 business days).
E-banking (Online Banking)
Ask a bank customer service agent how to use the online banking site. You will need to login from a secure server with your debit card information which requires a secure password. Do not share your password with anyone.
Credit Cards
Credit cards are used to borrow money from the bank to buy something. They are used to make payments in stores and online services, and require an application where you credit history is needed (how you have handled debt in the past). They are essentials for accessing some services, such as renting a car, purchasing an airline ticket, and online shopping, but fees may apply. If you choose to apply for a credit card, make sure you understand the terms, specifically with respect to interest charges.
How to Apply for a Credit Card
There are different types of credit cards which you can get from a bank or a credit card company. It is up to you to decide what the right card is for you. The newcomer package with your bank may offer a credit card option, and new citizens without credit history can apply for some of these cards such as for the RBC Cash Back Mastercard. Other financial institutions offer newcomers credit cards you can choose from. Information provided in an application for a card varies – make sure you know what documents you need.
How to Build Credit and Why it is Important for Everyone
In Canada, you will need a good credit history, and the best way to build credit in Canada is by using a credit card. Good credit is important when applying for a mortgage to buy a house, get a loan, or set up your own business. Credit Reporting Agencies track credit, and use this information to come up with your credit rating – this is like a financial report card for your credit history and shows other creditors, like a bank, whether you have a history of paying back your debts. This helps them make a decision whether it will be a good idea to sell you something where you pay back money over time.
Good Credit Card Practices – Use Your Credit Card Wisely
Use your credit card only to make purchases you know you can afford. Pay off your credit card balance in full each month (at least pay more than the minimum that owes), and make sure you do so on time.
- Ensure your payment has been received by the bank on or before the payment due date.
- Limit the number of credit cards you use and keep track of the money you owe.
- Don’t exceed the limit on your credit card, this impacts your credit score.
Paying Bills
You will need to pay the cost of services you use (cable/TV), rent, or credit cards on time. Pay attention on the due date. If a bill is not paid on time, service providers might send you a reminder. If reminders are not acknowledged, the service will be disconnected. If after reminders the bill is still unpaid, service providers might send the debt to a Collection Office which can use legal means to pursue the payment. This situation affects your credit history should be avoided.
Special Tips
- A landlord will not provide you with a reminder to pay your rent, and eviction is possible if rent is not paid on time.
- Long distance texting and calling abroad costs extra. Make sure you know the costs before making a call.
- Sort your bills by type of service (company) and keep the record of all your payments.
Budgeting
A budget is a plan that helps you manage your money and avoid getting into financial trouble. It lists all your income and expenses, and gives you an idea of your financial situation each month. It can keep you on track from spending more money than you really have. Try to balance your money between the things you “need” (e.g. rent, food, transit pass) and the things you “want” (e.g. a new laptop). The Government of Canada’s Budget Calculator is an excellent resource to help you with budgeting.
Special Tips
- Get organized: Record all of your spending so you know where your money goes and where you can cut spending (e.g. $3 coffee every day)
- Identify your short-term and long-term goals, and build saving for them into your budget (e.g. Short-term goal: buying a car; Long-term goal: retirement)
- Divide your expenses into two categories: things you “need”(e.g. food) and things you “want” (e.g. new laptop)
- Make “being debt-free” one of your goals (e.g. make a list of your debts and keep the record of your progress in paying them off)
- Pay more than the minimum payment on bills whenever you can (it reduces debt interests and the time to pay them off)
- Stick to your plan!
Looking for More Information?
Your settlement agency may provide workshops on finances. There are many programs available to help you manage and save your money:
Money Management Tool for Newcomers – This is an online tool developed by Prosper Canada to help newcomers assess their knowledge of the Canadian financial system and get customized money management information to help ease the transition.
Momentum
Centre for Family Literacy
See here for a list of community and non-profit organizations that are actively supporting the national strategy for financial literacy can be found.
Taxes
You are required to file your taxes with the government during the spring of each year. The Government of Canada provides important information for newcomers about the Canadian tax system, and your rights and responsibilities. Tax training and preparation assistance is also made available by your local settlement agency. Follow the links below to learn more about filing your taxes:
Canada Revenue Agency – Newcomers to Canada (Immigrants)
Canada Revenue Agency – Volunteer Tax Preparation Clinics
GST – Goods and Service Tax
Canadians pay taxes on goods and services. When you make a purchase, make sure you consider how much the tax will be on the item. This will not be included in the initial price. For more information, see the GST overview.
Travel Loans
When refugees travel to Canada, the Government of Canada pays for the associated flights and medical exam costs. This cost is covered by issuing loans if the refugee does not have the funds to cover their own costs. The Government requires that this transportation loan be repaid. The client will receive an account statement from IRCC (formally known as CIC) within a 5-8 month period and they are to start paying this loan back. It is a good idea to make a loan repayment schedule. Although you are responsible for repaying the loans, if you are a PSR, your sponsoring group can add the full or partial cost of the travel loan into their budget.
Please also note: the Government of Canada has waived this loan to the Syrian Refugees who arrived after Nov 4, 2015.
Click here more information on travel loans and Refugee Financial assistance.
Contact the Government of Canada – IRCC Help Centre for more information.
Scams
Scams are a dishonest way of making money by deceiving people. Please be aware of scams targeting newcomers. Exercise caution when you provide your credit card and banking information to people over the phone and in person. To prevent this from happening to you or your friends or family, please see for the below for more information:
What kinds of fraud should newcomers to Canada watch out for?
Related Articles
Money: Financial Literacy Helps Keep Finances and Relationships Healthy
Financial literacy leads to financial independence to newcomers
Knowing how to get around and access public transportation system is important in any city in Alberta. Public transportation operates slightly differently depending on where you are.
Tickets and passes can be purchased at downtown ticket vending machines, online, at a customer service centre, and some convenience and grocery stores. Please see below for city specific information.
Keep in mind rates vary depending for adults, youth and seniors. Low income monthly passes are also available, should you qualify.
Calgary
- The City of Calgary offers monthly transit passes at a reduced rate for low income Calgarians, including GARs on the RAP program at $44 per month.
- You must apply for the pass and provide photo ID. For more information, see: Low Income Monthly Pass
Edmonton
- If you are a recipient of the Provincial Assured Income for the Severely Handicapped, you are eligible for a subsidized pass. AISH Subsidized Transit Pass Program
Red Deer
- Red Deer Action Group – Subsidy Ride Program is offered by a not-for profit organization for certain travel costs.
Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
Instructions for Taking Transit
Want to learn how to take transit. This is a great instructional video presented by Ahlain.
Some seating on the bus or train is reserved for the elderly, families with young children and babies, pregnant women, and those with disabilities. Observe signs; do not sit in these seats if you are not elderly, pregnant, someone traveling with a family with young children and babies, or someone with a disability.
For your safety, when taking the train, be sure to keep a safe distance from the tracks.
When you are traveling with children, exercise caution on escalators. For your safety, DO NOT SIT on escalators.
Stand in designated waiting areas
On your journey, you may need to transfer. Be sure to accept a piece of paper to transfer from the bus driver if you pay cash for your ticket.
Taxi
If you are traveling with a large group, and going a short distance, it may be more economical to take a taxi. You can find a taxi by calling the company on the phone, or by signalling for one on the street. Both options are safe in Canada. It is common courtesy to tip your driver about 10 per cent minimum. Here are a few companies to choose from:
Calgary
Edmonton
Red Deer
Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
Brooks
Pedestrian Travel
Walking is another popular way to get from place to place in Alberta. Sidewalks and other pathways provide everyone with easy ways to get around the city. It is important to know the different rules and safety procedures for walking to and from places in Canada then. One of the most important is to watch for signals while walking. Below is a list of important signals to be aware about when commuting by foot.
Pedestrian Signals
Person: Walk. It is now safe for you to cross the street.
Hand: Do not cross. If the red hand is flashing, do not start to cross the street. If you have already started to cross, continue. When the hand is not blinking, do not start to cross the street.
Flashing green light or solid left-pointing arrow: Do not cross. A flashing green light or the arrow is a signal for drivers who want to turn left. This light only applies to drivers, but you should still follow cross walk light.
Crosswalk: Crosswalks are located at busy street corners where there is no stoplight. Push the button and wait for traffic to stop. Point your arm out in front of you to let drivers know that you want to cross.
Jay Walking
In Canada, it is illegal to jay walk. Jay walking is crossing the street at an area that does not have a defined cross walk. You can be fined for jay walking if caught by the police. This law helps protect your individual safety and prevent accidents from occurring.
Biking
Another healthy alternative mode of transportation system is biking. Many trails are available to help you get from one place to another using your bicycle. Some cities have specific lanes on the road available only for bicycling that are helpful to use at any time of the year. While biking, it is important to be safe and wear proper protection. Wearing a helmet while biking is the law, and it also helps prevent injury from falling on your head. If caught without a helmet by the police, you can be fined. Knowing your biking skill is also important, as you should not bike in areas that make you feel uncomfortable.
Some programs are available if you are interested in starting to bike, but lack funds to find a bike. Bicycles for Humanity is a charity that helps to provide bicycles to individuals in need, and should be contacted for help.
Driving
If you are driving, you’ll need an Alberta Driver’s license which you are required to carry with you when driving. This piece of identification is commonly used for other services. You will need to pass some tests to get a license. Driver Education is available for new drivers in Alberta to help you prepare for the tests, the Graduated Learning Test, and the advanced road test.
Here is a great video on driving in Alberta.
Traveling within Alberta
You can take the bus from city to city. Check out the following companies that offer affordable alternatives to flying or driving:
Greyhound
Red Arrow
Domestic Travel
If you plan to travel within Canada, you will need your Permanent Residency and refugee documents as well as a government issued photo ID, like a driver’s license.
International Travel
It is not recommended to travel outside of Canada before becoming a citizen to avoid any issues returning to the country.
If it is absolutely essential for you to travel outside of Canada as a permanent resident, you will need a passport from your country of citizenship, and a permanent resident card, issued by the Government of Canada. If you do not have a passport, apply for a refugee travel document. This can take several months, and it is recommended you do not make plans for international travel until documents are received.
Apply for a passport – adults
Transportation
Airlines
Air Canada
West Jet
For more information, consult the following Government of Canada website.
What is an Emergency?
An emergency is a serious, unexpected, and often dangerous situation requiring immediate attention. Some examples of emergencies requiring emergency services (ambulance, fire and police) include: house fire, sudden health circumstances that need urgent care like a heart attack or asthma, and other types of emergencies that are the result of instances such as a car accident, crime, domestic violence.
Please call 9-1-1 immediately if you need help from the police, fire or ambulance.
Here is a video on when to call 911.
For more information, see My Health Alberta.
For non-emergencies, contact a non-emergency line. Please find below your local non-emergency phone directory.
Calgary
Edmonton
Red Deer
Lethbridge
Medicine Hat
Brooks
Your Safety is Important
The police are here to serve and protect all individuals and their rights. The police work closely with all communities in Canada to build trusting relationships. Canada is consistently ranked in the top least corrupt countries in the world. You can ask the police for help in many types of situations, such as accidents, if you are a victim of assault, see a crime, or if someone has gone missing. The police are trusted points of contact for newcomers to Canada. Your local police are not just officers of the law, but also important community members helping to create a welcoming and inclusive society.
Please find below your local police service:
- Calgary Police Service
- Edmonton Police Service
- Red Deer Police Service
- Lethbridge Police Service
- Medicine Hat Police Service
- Brooks Police Service